How Advanced NDT Methods Improve Safety and Efficiency
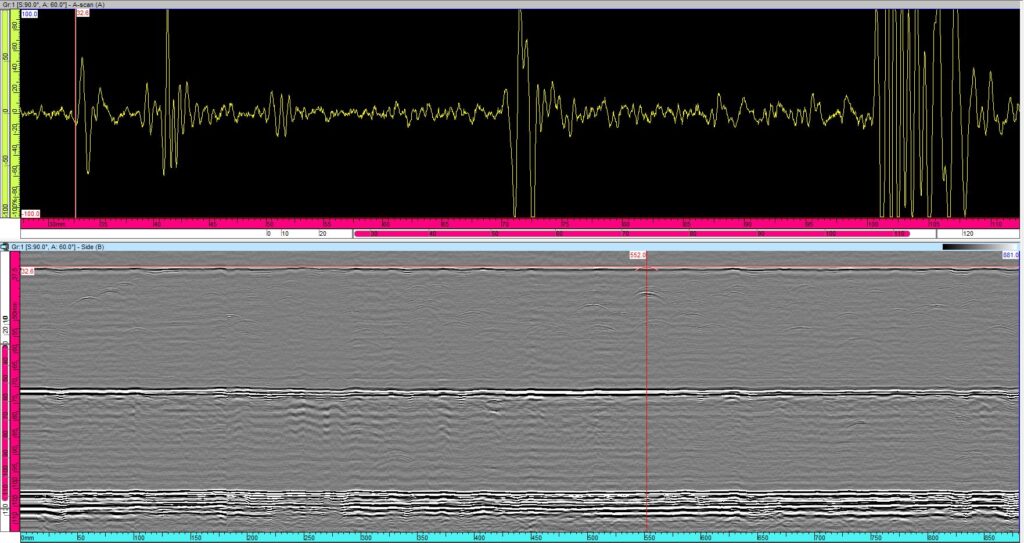
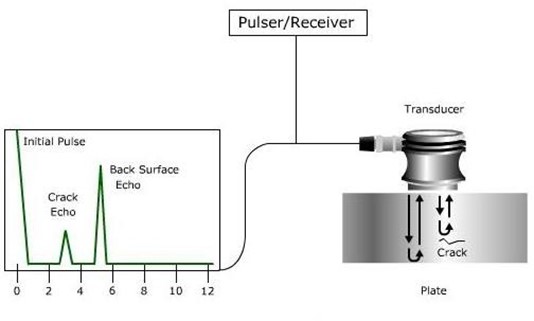
Non-destructive testing (NDT) plays a critical role in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and nuclear, ensuring the safety and longevity of infrastructure and equipment. With advancements in NDT technologies, industries are able to perform more accurate inspections, minimize downtime, and enhance operational safety. In this article, we explore real-world case studies where advanced NDT methods have made a significant impact.
1. Aerospace Industry: Enhancing Aircraft Safety
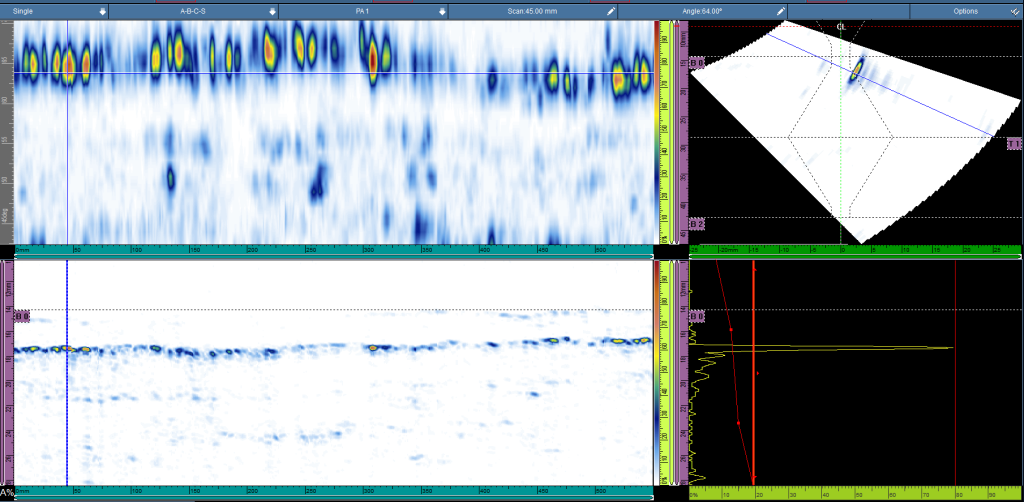
The aerospace industry demands the highest safety standards, making NDT essential for ensuring the structural integrity of aircraft. Advanced NDT methods such as phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT) and computed radiography have revolutionized the way aircraft components are inspected. One notable case involves the inspection of composite materials used in modern aircraft. Traditional inspection methods struggle with detecting defects in composites, but with PAUT, inspectors can accurately identify flaws within the material, such as delaminations or voids, without disassembling the aircraft.
In a case study involving a major airline, regular NDT inspections using advanced ultrasonic testing helped identify minor defects in critical structural components. These defects were detected early, preventing catastrophic failure and saving the airline millions in potential repair costs and operational downtime. Furthermore, the ability to detect these flaws non-invasively extended the life of the components, reducing the need for premature replacements.
2. Oil and Gas Industry: Preventing Catastrophic Failures
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on pipelines for the transportation of critical resources, making their integrity vital for safety and environmental protection. Corrosion under insulation (CUI) is a common issue in pipelines, where traditional visual inspections cannot detect hidden corrosion. Advanced NDT methods, such as infrared thermography and guided wave ultrasonic testing, have been used to inspect pipelines without the need to remove insulation or shut down operations.
In a recent case study, a major oil company employed advanced guided wave ultrasonic testing to inspect over 100 kilometers of pipelines in a remote area. The technology allowed the company to identify internal corrosion in sections that would have otherwise gone undetected until a potential failure occurred. By addressing the issue early, the company avoided significant environmental damage, financial loss, and legal repercussions.
Additionally, the use of drones equipped with infrared cameras for aerial inspections has further streamlined the inspection process. This technology enables the inspection of hard-to-reach areas, such as offshore platforms, without putting personnel at risk. In another case, drones helped identify pipeline leaks in a remote desert area, allowing for immediate repairs and preventing environmental contamination.
3. Nuclear Industry: Ensuring Structural Integrity in Extreme Conditions
The nuclear industry is perhaps the most stringent when it comes to safety, given the potentially catastrophic consequences of structural failure. Advanced NDT methods such as acoustic emission testing and computed tomography (CT) scanning have become essential for inspecting nuclear reactors and related infrastructure. These methods provide precise, real-time data on the condition of materials, allowing engineers to make informed decisions on maintenance and repairs.
In one case study, acoustic emission testing was used to monitor the structural health of a reactor vessel during a pressure test. The technology detected microcracks that were not visible through traditional methods, enabling the reactor to be safely decommissioned before the cracks could propagate and cause more significant damage.
Moreover, the use of robotic inspection systems in the nuclear industry has significantly reduced the risk to human inspectors. Robots equipped with NDT tools can perform inspections in hazardous environments, such as within radioactive containment areas, without exposing workers to dangerous levels of radiation.
4. Automotive Industry: Improving Vehicle Manufacturing and Safety
The automotive industry also benefits from advanced NDT technologies, especially in quality control during the manufacturing process. Automated ultrasonic testing systems and X-ray computed tomography are commonly used to inspect critical components such as engines, axles, and braking systems. These methods ensure that defects are detected early in the manufacturing process, reducing the risk of recalls and improving vehicle safety.
In a case study involving a major car manufacturer, automated ultrasonic testing was used to inspect the welds in vehicle frames. The technology identified several faulty welds that would have compromised the safety of the vehicles, allowing the manufacturer to address the issue before the vehicles were shipped to customers.
These case studies demonstrate the critical role of advanced NDT technologies in enhancing safety, reducing operational costs, and preventing failures across a variety of industries. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will further strengthen the ability of industries to maintain the integrity of their infrastructure, minimize environmental risks, and improve overall operational efficiency.


Professional Third-Party Inspection & Asset Integrity Inspection Services in Singapore
Ensure safety & compliance with expert Third-Party Inspection, Asset Integrity Inspection, In-Service Inspection, Storage Tank & Heat Treatment Inspection Services in Singapore. Cutech Group delivers reliable, certified inspections for industrial assets, ensuring operational efficiency & regulatory adherence.
For more details, Kindly visit us at : http://cutechgroup.com/inspectionservices.php