The Role of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) in the Shipbuilding Industry

In the shipbuilding industry, NDT is used to inspect the quality and condition of various materials and components used in the construction of ships.
Some common NDT techniques used in shipbuilding include ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and radiographic testing. These techniques allow engineers and technicians to detect defects, such as cracks or weld imperfections, that could affect the strength and integrity of the ship.

Most common NDT methods in ship building
There are several NDT methods that are commonly used in the shipbuilding industry, including:
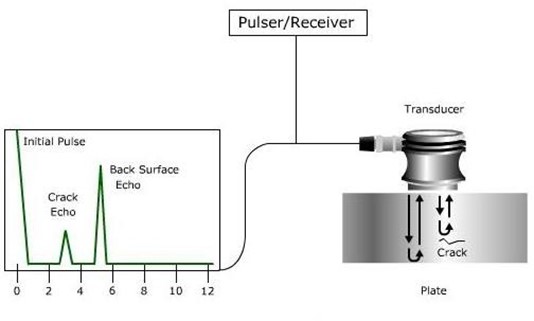
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): UT involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to inspect the thickness and integrity of materials. It is often used to inspect welds, as well as to measure the thickness of steel plates and other structural components.
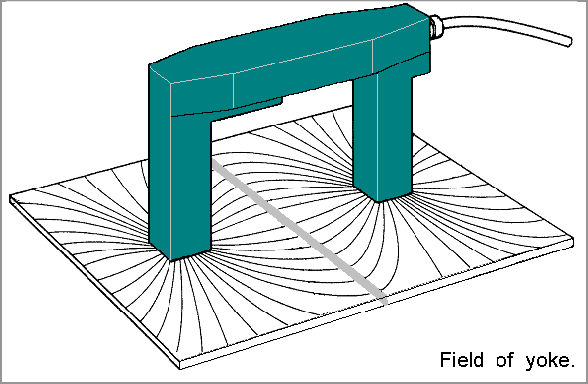
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): MPI involves the use of a magnetic field and iron oxide or iron oxide-coated magnetic particles to detect surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): RT involves the use of x-rays or gamma rays to inspect materials for internal defects. It is often used to inspect welds and castings.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT): LPT involves the application of a liquid penetrant to the surface of a material, which is then drawn into any surface-breaking defects by capillary action. Excess penetrant is then removed, and a developer is applied, which helps to highlight the defects.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): ECT involves the use of eddy currents, which are induced currents that flow in the opposite direction of the inducing current, to inspect conductive materials for surface and slightly subsurface defects.
- Visual Testing (VT): VT involves the examination of the surface of a material using the naked eye or with the aid of a magnifying device. It is often used in conjunction with other NDT methods to verify the results or to provide additional information about the defect.
What is inspected on ships?
NDT is used to inspect a wide range of materials and components on ships, including:
- Welds: Welds are used extensively in the construction of ships, and NDT is used to ensure that they are free of defects such as cracks, porosity, and incomplete fusion.
- Steel plates and structural components: NDT is used to inspect steel plates and structural components, such as beams and girders, for thickness and integrity.
- Machinery and equipment: NDT is used to inspect machinery and equipment, such as engines and generators, for wear, corrosion, and other types of damage.
- Hull and deck structures: NDT is used to inspect the hull and deck structures of a ship for corrosion, fatigue, and other types of damage that could compromise the strength and integrity of the vessel.
- Electrical and electronic systems: NDT is used to inspect electrical and electronic systems, such as wiring and circuit boards, for defects and damage.
- Pipes and piping systems: NDT is used to inspect pipes and piping systems, such as fuel lines and hydraulic lines, for corrosion, erosion, and other types of damage.
NDT and ship maintenance
NDT is used as a maintenance tool to help ensure the safe and reliable operation of ships. Some of the ways that NDT is used for maintenance on ships include:
- Periodic inspections: Many components on a ship, such as welds and structural elements, need to be inspected at regular intervals to ensure that they are in good condition. NDT is often used for these periodic inspections because it allows technicians to evaluate the condition of the components without having to disassemble them or cause any damage.
- Troubleshooting: If a problem or malfunction is detected on a ship, NDT can be used to help identify the cause. For example, if an engine is not running correctly, NDT could be used to inspect the engine components for defects or damage.
- Condition monitoring: NDT can be used to monitor the condition of various components on a ship over time. By performing periodic NDT inspections, technicians can track the progression of any defects or damage and take appropriate action before the problem becomes more serious.
- Predictive maintenance: Some NDT techniques, such as vibration analysis and ultrasonic testing, can be used to predict when a component is likely to fail. This allows maintenance personnel to schedule repairs or replacements before the component fails, which can help to reduce downtime and improve the overall reliability of the ship.
Hull inspection
NDT is often used to inspect the hull of a ship for various types of damage, such as corrosion, fatigue, and impact damage. Some of the NDT techniques that may be used to inspect the hull of a ship include:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): to inspect the thickness and integrity of the hull plating. It can detect corrosion, pitting, and other types of surface and subsurface defects.
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): to detect surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities in the hull plating. It is particularly useful for detecting cracks, which can be a common form of damage on the hull of a ship.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): to inspect the hull plating for surface and slightly subsurface defects. It is particularly useful for detecting corrosion, which can weaken the hull and compromise the structural integrity of the ship.
- Visual Testing (VT): It is often used in conjunction with other NDT methods to verify the results or to provide additional information about the condition of the hull.
Advantages of NDT in ship maintenance inspection
There are several advantages to using NDT for maintenance and inspection on ships, including:
- Efficiency: NDT allows technicians to quickly and accurately evaluate the condition of various components and materials on a ship without having to disassemble or dismantle them. This can save a significant amount of time and labor compared to traditional inspection methods.
- Cost savings: NDT can be more cost-effective than traditional inspection methods because it does not require the removal or replacement of components. This can help to reduce maintenance costs and downtime.
- Safety: NDT does not involve the use of hazardous materials or processes, and it does not require the removal or handling of heavy components. This makes it a safer option for technicians compared to traditional inspection methods.
- Non-invasive: NDT allows technicians to evaluate the condition of components and materials without causing any damage, which is particularly important for components that are difficult or costly to replace.
- Accuracy: NDT techniques are highly accurate and reliable, which helps to ensure that defects and problems are detected and addressed in a timely manner. This can help to reduce the risk of equipment failure and improve the overall reliability of the ship.
Cracking and Fatigue defects
Cracking and fatigue are two common types of damage that can occur in ships and can lead to disasters if not properly addressed. Some examples of ship disasters that have been caused by cracking or fatigue include:
- The sinking of the RMS Titanic: This famous ship disaster was caused in part by the failure of a weld in the hull, which allowed water to flood into the ship and sink it.
- The sinking of the MV Sewol: This ferry disaster was caused by the failure of a number of welds in the hull, which allowed the ship to capsize and sink.
- The explosion of the Deepwater Horizon oil rig: This disaster was caused by a failure in the casing of an oil well, which allowed oil and gas to leak out and ignite.
- The capsizing of the M/V Cougar Ace: This cargo ship disaster was caused by the failure of a number of welds in the hull, which allowed the ship to capsize and roll over.
- The sinking of the M/V Dona Paz: This passenger ferry disaster was caused by a collision with another vessel, which caused a number of welds in the hull to fail and allow water to flood into the ship.
Why perform NDT on ships?
There are several reasons why NDT is performed on ships:
- To ensure the safety and reliability of the ship: NDT is used to identify defects and damage in materials and components on a ship that could compromise its strength, integrity, and overall performance. By detecting and addressing these issues, NDT helps to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the ship.
- To extend the life of the ship: By identifying and addressing problems early, NDT can help to extend the service life of a ship. This can help to reduce the need for repairs and replacements, which can save money and reduce downtime.
- To meet regulatory requirements: Many countries have regulations that require ships to undergo periodic inspections to ensure that they are in good condition and safe to operate. NDT is often used to meet these inspection requirements.
- To improve efficiency: NDT can help to identify problems that are causing equipment to operate inefficiently or to malfunction. By addressing these issues, NDT can help to improve the overall efficiency of the ship.
- To reduce maintenance costs: NDT can help to reduce maintenance costs by identifying and addressing problems before they become more serious. This can help to reduce the need for costly repairs and replacements, as well as reduce downtime.
10 largest ships in the world
- Prelude FLNG: This floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is 488 meters long and 74 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 696,000 GT.
- Pioneering Spirit: This is a pipelaying and decommissioning vessel that is 382 meters long and 124 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 382,000 GT.
- Seawise Giant: This was a ULCC supertanker that was 458.45 meters long and 69.8 meters wide. It had a gross tonnage of 564,763 GT.
- Knock Nevis: This was also a ULCC supertanker that was 458.45 meters long and 69.8 meters wide. It had a gross tonnage of 564,763 GT.
- Emma Maersk: This container ship is 397 meters long and 56 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 159,000 GT.
- Pioneering Spirit: This is a pipelaying and decommissioning vessel that is 382 meters long and 124 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 382,000 GT.
- Knock Nevis: This was a ULCC supertanker that was 458.45 meters long and 69.8 meters wide. It had a gross tonnage of 564,763 GT.
- Seawise Giant: This was also a ULCC supertanker that was 458.45 meters long and 69.8 meters wide. It had a gross tonnage of 564,763 GT.
- Prelude FLNG: This floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is 488 meters long and 74 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 696,000 GT.
- Emma Maersk: This container ship is 397 meters long and 56 meters wide. It has a gross tonnage of 159,000 GT.


Responses