Emerging NDT Technologies: A Revolution in Non-Destructive Testing

Non-destructive testing (NDT) has undergone significant advancements with the integration of emerging technologies. These innovations are transforming the industry, making inspections more efficient, accurate, and comprehensive. In this article, we will explore key emerging technologies that are reshaping NDT practices and how they are driving the future of industrial inspections.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in NDT
One of the most exciting developments in NDT is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies enable advanced data analysis, identifying patterns in complex datasets that humans might overlook. Here are some key applications:
- Data Processing Automation: AI algorithms can automate data collection and analysis, reducing the need for manual interpretation of inspection results. This leads to faster and more accurate defect identification.
- Predictive Maintenance: Machine learning models can analyze historical inspection data to predict when equipment or infrastructure might fail. This allows companies to schedule preventive maintenance, minimizing downtime and costly repairs.
- Image Recognition and Pattern Detection: AI is also improving the accuracy of visual inspections by automatically recognizing defects in images or videos. For instance, AI can analyze ultrasonic, radiographic, or infrared data, identifying potential issues more quickly than a human inspector.
2. Robotics and Drones for Remote Inspections
Robotic technologies are making NDT safer and more accessible, particularly in hazardous environments. Drones and robotics are now commonly used for:
- Aerial Inspections: Drones equipped with NDT tools (such as infrared cameras or ultrasonic sensors) can inspect hard-to-reach areas, like tall structures, pipelines, or offshore platforms. This reduces the risk to human inspectors and speeds up the inspection process.
- Subsea Inspections: Remote-operated vehicles (ROVs) are used for underwater inspections of subsea pipelines, oil rigs, and other infrastructure. These robots can perform detailed visual inspections and collect data without the need for divers.
- Autonomous Inspection Systems: Ground-based robots equipped with NDT sensors can autonomously scan large areas, such as industrial plants or power stations. These systems can operate continuously, providing real-time data and reducing the need for manual inspections.
3. Advanced Imaging and Sensing Technologies
Emerging imaging technologies are enabling more detailed and precise inspections. These include:
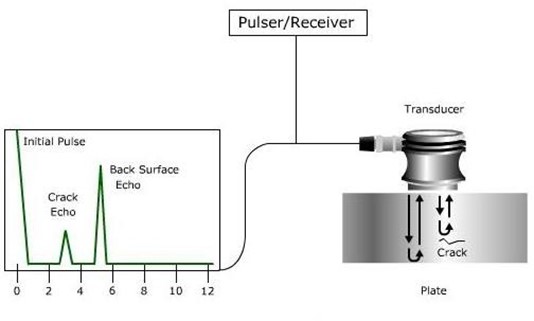
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT): This advanced form of ultrasonic testing uses multiple sound beams to inspect materials at various angles. It offers greater accuracy and faster inspections compared to traditional methods.
- Terahertz Imaging: Terahertz (THz) imaging is a cutting-edge technology that uses electromagnetic waves to detect defects in non-metallic materials, such as composites used in the aerospace industry. It is non-invasive and can detect defects that are invisible to other methods.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning: CT scanning is commonly used in the medical field, but it is gaining traction in NDT for inspecting complex industrial components. CT provides 3D images of internal structures, allowing for precise defect detection and analysis.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-Time Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming NDT by enabling real-time monitoring of critical infrastructure. IoT-connected sensors can continuously collect data from structures like bridges, pipelines, and industrial equipment. This data is transmitted in real-time to a central monitoring system, allowing for:
- Continuous Structural Health Monitoring: Sensors embedded in materials can monitor stress, strain, and temperature changes over time. This allows for proactive maintenance and reduces the risk of catastrophic failures.
- Remote Data Access: IoT systems allow inspectors and engineers to access inspection data remotely, streamlining decision-making processes and reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Enhanced Safety: By using IoT for continuous monitoring, dangerous conditions can be detected early, reducing the risk of accidents in high-risk environments.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) for Training and Inspections
AR and VR technologies are being integrated into NDT training and operations. These tools are improving the training process and allowing inspectors to visualize inspection data in new ways:
- Training Simulations: VR simulations provide realistic, immersive environments for NDT trainees to practice their skills. These simulations mimic real-world inspection scenarios, enabling inspectors to gain experience without risking safety.
- Augmented Reality for Inspections: AR overlays digital information onto the real world, assisting inspectors in visualizing hidden defects, guiding them through complex inspection processes, or displaying real-time data from sensors.
The integration of emerging technologies into non-destructive testing is revolutionizing the industry, making inspections more efficient, accurate, and safer. AI, robotics, drones, advanced imaging, IoT, and AR/VR are just a few of the innovations that are reshaping NDT practices across industries like aerospace, oil and gas, and construction. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect NDT to become even more critical in ensuring the safety and integrity of infrastructure and equipment around the world.
By staying updated on these advancements, businesses can harness these technologies to improve their inspection processes, enhance safety, and reduce operational costs.



Responses