NDT Standards: A Guide to the Organizations and Regulations Governing NDT

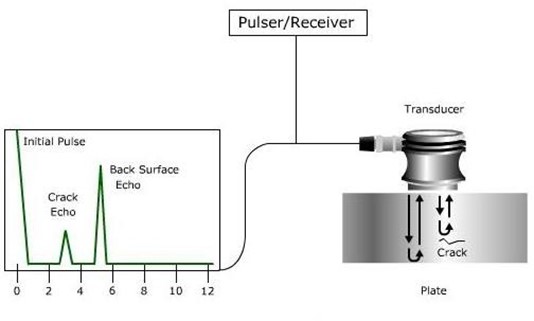
NDT, or non-destructive testing, refers to a variety of techniques used to evaluate the properties of a material, component, or system without causing damage. There are many different NDT methods, including ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, and visual testing, among others.

NDT methods are used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and manufacturing, to ensure the quality and safety of products. NDT is also used to inspect and monitor the condition of structures and systems, such as bridges, pipelines, and aircraft.
There are several organizations that develop and publish standards for NDT, including the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT), the British Society for Non-Destructive Testing (BSNDT), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for the training, certification, and performance of NDT personnel, as well as the proper use and interpretation of NDT techniques.
NDT standards in Europe
In Europe, NDT standards are developed and published by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN), which is a network of national standardization organizations from 33 European countries. CEN works to develop and promote European standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of European NDT standards published by CEN include:
- EN 473: Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- EN ISO 9712: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- EN ISO 13588: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to the European Union.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in Europe, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. EN 4179), the automotive industry (e.g. EN ISO 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. EN 13791). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by CEN.
NDT standards in UK
In Britain, NDT standards are developed and published by the British Standards Institution (BSI), which is the national standards organization of the United Kingdom. BSI works to develop and promote British standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of British NDT standards published by BSI include:
- BS EN 473: Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- BS EN ISO 9712: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- BS EN ISO 13588: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to the United Kingdom.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in Britain, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. BS EN 4179), the automotive industry (e.g. BS EN ISO 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. BS EN 13791). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by BSI.
NDT standards in US
In the United States, NDT standards are developed and published by the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT), which is a professional society for NDT practitioners and technicians. ASNT works to advance the field of NDT through the development and promotion of standards, as well as through education and training programs.
Some examples of American NDT standards published by ASNT include:
- SNT-TC-1A: Personnel Qualification and Certification in Nondestructive Testing
- CP-189: ASNT Standard for Qualification and Certification of Nondestructive Testing Personnel
- AC-7B: Standard for Qualification and Certification of NDT Inspection Agencies
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to the United States.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in the United States, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. NAS 410), the automotive industry (e.g. ISO/TS 16949), and the construction industry (e.g. ASTM E329). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by ASNT.
ISO NDT standards
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is an international standardization organization that develops and publishes standards for a wide range of industries, including NDT. ISO NDT standards provide guidelines for the proper use and interpretation of NDT techniques, as well as for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel.
Some examples of ISO NDT standards include:
- ISO 9712: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- ISO 13588: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
- ISO 15549: Non-destructive testing – ultrasonic testing – shear wave testing
These standards are widely recognized and used in many countries around the world, and are often adopted as national standards by countries that are members of ISO. In addition to these general NDT standards, there are also many sector-specific ISO NDT standards, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. ISO 17359), the automotive industry (e.g. ISO 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. ISO 12706). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general ISO NDT standards.
Canada NDT standards
In Canada, NDT standards are developed and published by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), which is a national standards organization that works to develop and promote standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of Canadian NDT standards published by the CSA include:
- CAN/CSA-SNT-TC-1A: Personnel Qualification and Certification in Non-destructive Testing
- CAN/CSA-CP-189: CSA Standard for Qualification and Certification of Non-destructive Testing Personnel
- CAN/CSA-N287.3: Non-destructive Testing – Qualification and Certification of Inspection Agencies
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to Canada.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in Canada, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. CAN/CSA-S-531), the automotive industry (e.g. CAN/CSA-ISO 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. CAN/CSA-S806). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by the CSA.
NDT standards in Australia
In Australia, NDT standards are developed and published by Standards Australia, which is a national standards organization that works to develop and promote standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of Australian NDT standards published by Standards Australia include:
- AS/NZS 4376:2005: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- AS/NZS ISO 9712:2019: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- AS/NZS ISO 13588:2019: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to Australia.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in Australia, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. AS/NZS 4643), the automotive industry (e.g. AS/NZS ISO 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. AS 5388). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by Standards Australia.
NDT standards South Africa
In South Africa, NDT standards are developed and published by the South African Bureau of Standards (SABS), which is a national standards organization that works to develop and promote standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of South African NDT standards published by the SABS include:
- SANS 1239: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- SANS 5759: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
- SANS 10147: Non-destructive testing – Ultrasonic testing
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to South Africa.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in South Africa, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. SANS 4179), the automotive industry (e.g. SANS 16810), and the construction industry (e.g. SANS 13791). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by the SABS.
India NDT standards
In India, NDT standards are developed and published by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), which is a national standards organization that works to develop and promote standards in a variety of fields, including NDT.
Some examples of Indian NDT standards published by the BIS include:
- IS-13539: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT personnel
- IS-13540: Non-destructive testing – Qualification and certification of NDT inspection agencies
- IS-10307: Non-destructive testing – Ultrasonic testing
These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, as well as the accreditation of NDT inspection agencies. They are based on international standards, such as ISO 9712 and ISO 13588, but may include additional requirements specific to India.
In addition to these standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards in India, such as those for the aerospace industry (e.g. IS-5159), the automotive industry (e.g. IS-16810), and the construction industry (e.g. IS-13791). These standards provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in these industries, and may be used in conjunction with the general NDT standards published by the BIS.
There are several organizations that develop and publish NDT standards, including the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT), the British Society for Non-Destructive Testing (BSNDT), the European Committee for Standardization (CEN), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), Standards Australia, the South African Bureau of Standards (SABS), and the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
These standards provide guidelines for the training, certification, and performance of NDT personnel, as well as the proper use and interpretation of NDT techniques.
In addition to general NDT standards, there are also many sector-specific NDT standards that provide specific requirements for the use of NDT in different industries.
Stay current on NDT codes and standards and engage in discussions by joining our NDT Codes and Standards forum and group.
Subscribe to our newsletter!



Responses