Time of Flight Diffraction (ToFD)
Welcome to [NDT Inspection Portal]’s time of flight diffraction (ToFD) group, a place for professionals... View more
TOFD Basic Theory
TOFD Basic Theory
TOFD Basic Theory
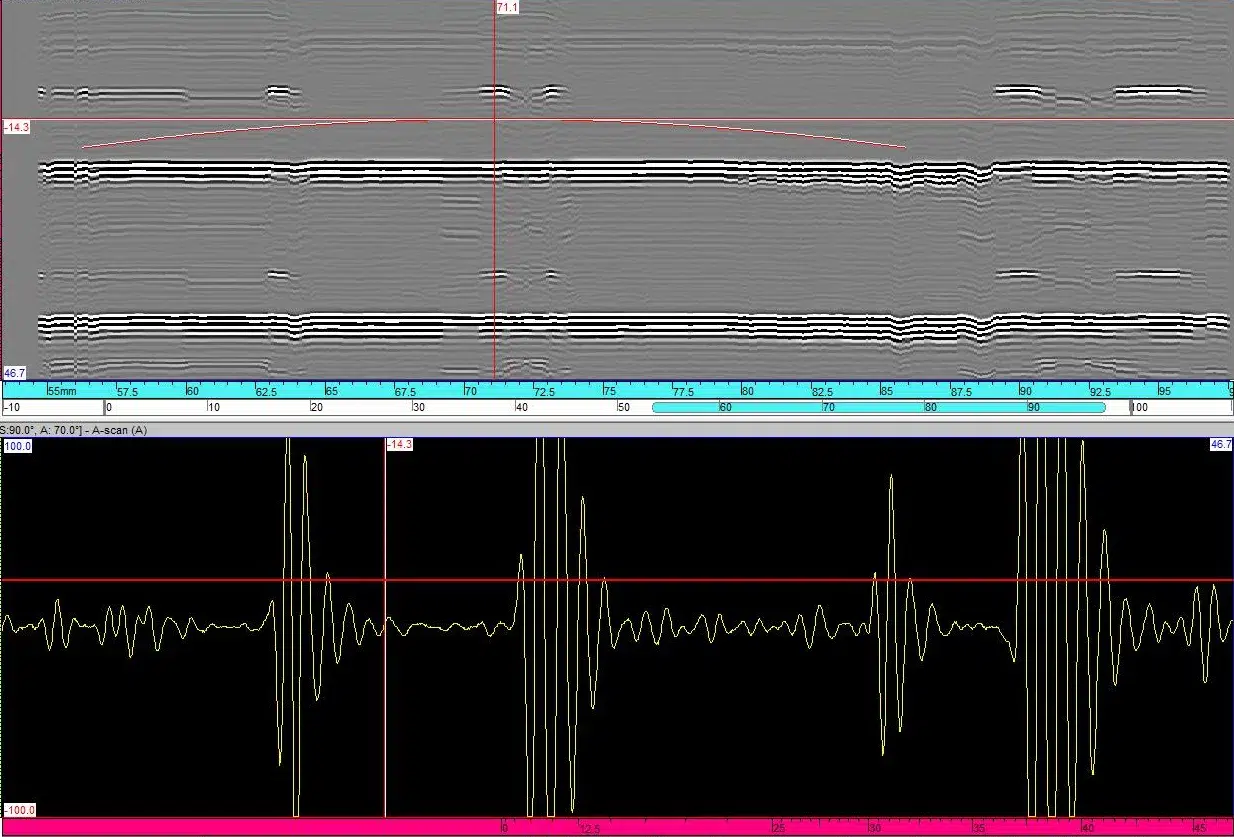
TOFD is usually performed using longitudinal waves as the primary detection method. Ultrasonic sensors are placed on each side of the weld. One sensor sends the ultrasonic beam into the material and the other sensor receives reflected and diffracted ultrasound from anomalies and geometric reflectors. TOFD provides a wide area of coverage with a single beam by exploiting ultrasonic beam spread theory inside the wedge and the inspected material. When the beam comes in contact with the tip of a flaw, or crack, diffracted energy is cast in all directions. Measuring the time of flight of the diffracted beams enables accurate and reliable flaw detection and sizing, even if the crack is off-oriented to the intial beam direction. During typical TOFD inspections, A-scans are collected and used to create B-scan (side view) images of the weld. Analysis is done on the acquisition unit or in post-analysis software, positioning cursors to measure the length and through-wall height of flaws.
Sorry, there were no replies found.
Log in to reply.